McqMate
550+ Data Structures (DS) Solved MCQs
These multiple-choice questions (MCQs) are designed to enhance your knowledge and understanding in the following areas: Computer Science Engineering (CSE) , Information Technology Engineering (IT) , Bachelor of Science in Computer Science FY (BSc CS) , Bachelor of Science in Information Technology FY (BSc IT) , Bachelor of Computer Applications (BCA) .
Chapters
| 51. |
Circular Queue is also known as |
| A. | Ring Buffer |
| B. | Square Buffer |
| C. | Rectangle Buffer |
| D. | Curve Buffer |
| Answer» A. Ring Buffer | |
| 52. |
If the elements “A”, “B”, “C” and “D” are placed in a queue and are deleted one at a time, in what order will they be removed? |
| A. | ABCD |
| B. | DCBA |
| C. | DCAB |
| D. | ABDC |
| Answer» A. ABCD | |
| 53. |
A data structure in which elements can be inserted or deleted at/from both the ends but not in the middle is? |
| A. | Queue |
| B. | Circular queue |
| C. | Dequeue |
| D. | Priority queue |
| Answer» C. Dequeue | |
| 54. |
A normal queue, if implemented using an array of size MAX_SIZE, gets full when |
| A. | Rear = MAX_SIZE – 1 |
| B. | Front = (rear + 1)mod MAX_SIZE |
| C. | Front = rear + 1 |
| D. | Rear = front |
| Answer» A. Rear = MAX_SIZE – 1 | |
| 55. |
Queues serve major role in |
| A. | Simulation of recursion |
| B. | Simulation of arbitrary linked list |
| C. | Simulation of limited resource allocation |
| D. | Simulation of heap sort |
| Answer» C. Simulation of limited resource allocation | |
| 56. |
Which of the following is not the type of queue? |
| A. | Ordinary queue |
| B. | Single ended queue |
| C. | Circular queue |
| D. | Priority queue |
| Answer» B. Single ended queue | |
| 57. |
With what data structure can a priority queue be implemented? |
| A. | Array |
| B. | List |
| C. | Heap |
| D. | Tree |
| Answer» D. Tree | |
| 58. |
Which of the following is not an application of priority queue? |
| A. | Huffman codes |
| B. | Interrupt handling in operating system |
| C. | Undo operation in text editors |
| D. | Bayesian spam filter |
| Answer» C. Undo operation in text editors | |
| 59. |
What is the time complexity to insert a node based on key in a priority queue? |
| A. | O(nlogn) |
| B. | O(logn) |
| C. | O(n) |
| D. | O(n2) |
| Answer» C. O(n) | |
| 60. |
What is not a disadvantage of priority scheduling in operating systems? |
| A. | A low priority process might have to wait indefinitely for the CPU |
| B. | If the system crashes, the low priority systems may be lost permanently |
| C. | Interrupt handling |
| D. | Indefinite blocking |
| Answer» C. Interrupt handling | |
| 61. |
Which of the following is not an advantage of priority queue? |
| A. | Easy to implement |
| B. | Processes with different priority can be efficiently handled |
| C. | Applications with differing requirements |
| D. | Easy to delete elements in any case |
| Answer» D. Easy to delete elements in any case | |
| 62. |
What is the time complexity to insert a node based on position in a priority queue? |
| A. | O(nlogn) |
| B. | O(logn) |
| C. | O(n) |
| D. | O(n2) |
| Answer» C. O(n) | |
| 63. |
What is a dequeue? |
| A. | A queue with insert/delete defined for both front and rear ends of the queue |
| B. | A queue implemented with a doubly linked list |
| C. | A queue implemented with both singly and doubly linked lists |
| D. | A queue with insert/delete defined for front side of the queue |
| Answer» A. A queue with insert/delete defined for both front and rear ends of the queue | |
| 64. |
What are the applications of dequeue? |
| A. | A-Steal job scheduling algorithm |
| B. | Can be used as both stack and queue |
| C. | To find the maximum of all sub arrays of size k |
| D. | To avoid collision in hash tables |
| Answer» D. To avoid collision in hash tables | |
| 65. |
Which of the following properties is associated with a queue? |
| A. | First In Last Out |
| B. | First In First Out |
| C. | Last In First Out |
| D. | Last In Last Out |
| Answer» B. First In First Out | |
| 66. |
In a circular queue, how do you increment the rear end of the queue? |
| A. | rear++ |
| B. | (rear+1) % CAPACITY |
| C. | (rear % CAPACITY)+1 |
| D. | rear– |
| Answer» B. (rear+1) % CAPACITY | |
| 67. |
What is the term for inserting into a full queue known as? |
| A. | overflow |
| B. | underflow |
| C. | null pointer exception |
| D. | program won’t be compiled |
| Answer» A. overflow | |
| 68. |
What is the need for a circular queue? |
| A. | effective usage of memory |
| B. | easier computations |
| C. | to delete elements based on priority |
| D. | implement LIFO principle in queues |
| Answer» A. effective usage of memory | |
| 69. |
What is the space complexity of a linear queue having n elements? |
| A. | O(n) |
| B. | O(nlogn) |
| C. | O(logn) |
| D. | O(1) |
| Answer» A. O(n) | |
| 70. |
What is the maximum number of children that a binary tree node can have? |
| A. | 0 |
| B. | 1 |
| C. | 2 |
| D. | 3 |
| Answer» C. 2 | |
| 71. |
The following given tree is an example for?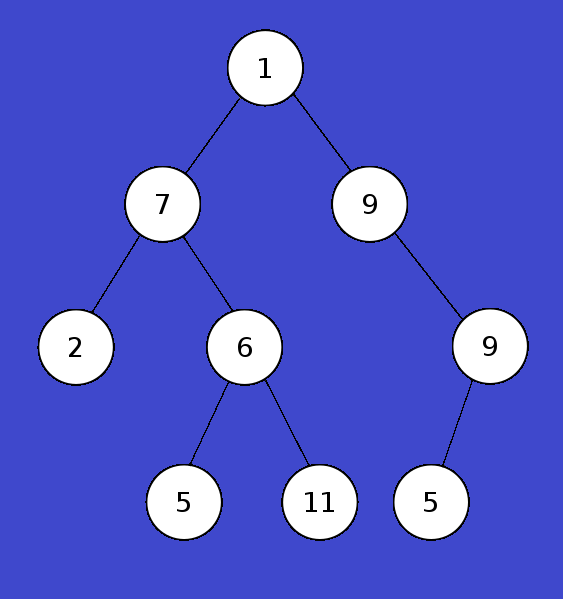
|
| A. | Binary tree |
| B. | Binary search tree |
| C. | Fibonacci tree |
| D. | none |
| Answer» A. Binary tree | |
| 72. |
How many common operations are performed in a binary tree? |
| A. | 1 |
| B. | 2 |
| C. | 3 |
| D. | 4 |
| Answer» C. 3 | |
| 73. |
What is the traversal strategy used in the binary tree? |
| A. | depth-first traversal |
| B. | breadth-first traversal |
| C. | random traversal |
| D. | Priority traversal |
| Answer» B. breadth-first traversal | |
| 74. |
How many types of insertion are performed in a binary tree? |
| A. | 1 |
| B. | 2 |
| C. | 3 |
| D. | 4 |
| Answer» B. 2 | |
| 75. |
What operation does the following diagram depict?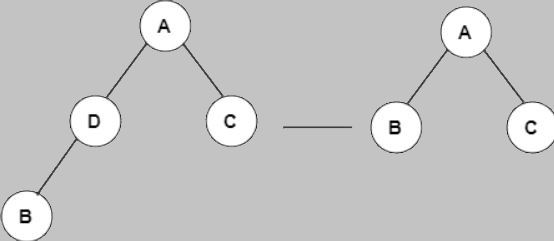
|
| A. | inserting a leaf node |
| B. | inserting an internal node |
| C. | deleting a node with 0 or 1 child |
| D. | none |
| Answer» C. deleting a node with 0 or 1 child | |
| 76. |
How many bits would a succinct binary tree occupy? |
| A. | n+O(n) |
| B. | 2n+O(n) |
| C. | n/2 |
| D. | n |
| Answer» B. 2n+O(n) | |
| 77. |
The average depth of a binary tree is given as? |
| A. | O(N) |
| B. | O(√N) |
| C. | O(N2) |
| D. | O(log N) |
| Answer» D. O(log N) | |
| 78. |
How many orders of traversal are applicable to a binary tree (In General)? 3 |
| A. | 1 |
| B. | 4 |
| C. | 2 |
| D. | 3 |
| Answer» D. 3 | |
| 79. |
If binary trees are represented in arrays, what formula can be used to locate a left child, if the node has an index i? |
| A. | 2i+1 |
| B. | 2i+2 |
| C. | 2i |
| D. | 4i |
| Answer» A. 2i+1 | |
| 80. |
Using what formula can a parent node be located in an array? |
| A. | (i+1)/2 |
| B. | (i-1)/2 |
| C. | i/2 |
| D. | 2i/2 |
| Answer» B. (i-1)/2 | |
| 81. |
Which of the following properties are obeyed by all three tree – traversals? |
| A. | Left subtrees are visited before right subtrees |
| B. | Right subtrees are visited before left subtrees |
| C. | Root node is visited before left subtree |
| D. | Root node is visited before right subtree |
| Answer» A. Left subtrees are visited before right subtrees | |
| 82. |
For the tree below, write the pre-order traversal. |
| A. | 2, 7, 2, 6, 5, 11, 5, 9, 4 |
| B. | 2, 7, 5, 2, 6, 9, 5, 11, 4 |
| C. | 2, 5, 11, 6, 7, 4, 9, 5, 2 |
| D. | none |
| Answer» A. 2, 7, 2, 6, 5, 11, 5, 9, 4 | |
| 83. |
For the tree below, write the post-order traversal. |
| A. | 2, 7, 2, 6, 5, 11, 5, 9, 4 |
| B. | 2, 7, 5, 2, 6, 9, 5, 11, 4 |
| C. | 2, 5, 11, 6, 7, 4, 9, 5, 2 |
| D. | none |
| Answer» C. 2, 5, 11, 6, 7, 4, 9, 5, 2 | |
| 84. |
What is the time complexity of pre-order traversal in the iterative fashion? |
| A. | O(1) |
| B. | O(n) |
| C. | O(logn) |
| D. | O(nlogn) |
| Answer» B. O(n) | |
| 85. |
What is the space complexity of the post-order traversal in the recursive fashion? (d is the tree depth and n is the number of nodes) |
| A. | O(1) |
| B. | O(nlogd) |
| C. | O(logd) |
| D. | O(d) |
| Answer» D. O(d) | |
| 86. |
To obtain a prefix expression, which of the tree traversals is used? |
| A. | Level-order traversal |
| B. | Pre-order traversal |
| C. | Post-order traversal |
| D. | In-order traversal |
| Answer» B. Pre-order traversal | |
| 87. |
Consider the following data. The pre order traversal of a binary tree is A, B, E, C, D. The in order traversal of the same binary tree is B, E, A, D, C. The level order sequence for the binary tree is |
| A. | A, C, D, B, E |
| B. | A, B, C, D, E |
| C. | A, B, C, E, D |
| D. | D, B, E, A, C |
| Answer» B. A, B, C, D, E | |
| 88. |
What is the possible number of binary trees that can be created with 3 nodes, giving the sequence N, M, L when traversed in post-order. |
| A. | 15 |
| B. | 3 |
| C. | 5 |
| D. | 8 |
| Answer» C. 5 | |
| 89. |
The post-order traversal of a binary tree is O P Q R S T. Then possible pre-order traversal will be |
| A. | T Q R S O P |
| B. | T O Q R P S |
| C. | T Q O P S R |
| D. | T Q O S P R |
| Answer» C. T Q O P S R | |
| 90. |
A binary search tree contains values 7, 8, 13, 26, 35, 40, 70, 75. Which one of the following is a valid post-order sequence of the tree provided the pre-order sequence as 35, 13, 7, 8, 26, 70, 40 and 75? |
| A. | 7, 8, 26, 13, 75, 40, 70, 35 |
| B. | 26, 13, 7, 8, 70, 75, 40, 35 |
| C. | 7, 8, 13, 26, 35, 40, 70, 75 |
| D. | 8, 7, 26, 13, 40, 75, 70, 35 |
| Answer» D. 8, 7, 26, 13, 40, 75, 70, 35 | |
| 91. |
Which of the following pair’s traversals on a binary tree can build the tree uniquely? |
| A. | post-order and pre-order |
| B. | post-order and in-order |
| C. | post-order and level order |
| D. | level order and preorder |
| Answer» B. post-order and in-order | |
| 92. |
A full binary tree can be generated using |
| A. | post-order and pre-order traversal |
| B. | pre-order traversal |
| C. | post-order traversal |
| D. | in-order traversal |
| Answer» A. post-order and pre-order traversal | |
| 93. |
The maximum number of nodes in a tree for which post-order and pre-order traversals may be equal is |
| A. | 3 |
| B. | 1 |
| C. | 2 |
| D. | any number |
| Answer» B. 1 | |
| 94. |
The pre-order and in-order are traversals of a binary tree are T M L N P O Q and L M N T O P Q. Which of following is post-order traversal of the tree? |
| A. | L N M O Q P T |
| B. | N M O P O L T |
| C. | L M N O P Q T |
| D. | O P L M N Q T |
| Answer» A. L N M O Q P T | |
| 95. |
Find the postorder traversal of the binary tree shown below. |
| A. | P Q R S T U V W X |
| B. | W R S Q P V T U X |
| C. | S W T Q X U V R P |
| D. | none |
| Answer» C. S W T Q X U V R P | |
| 96. |
For the tree below, write the in-order traversal. |
| A. | 6, 2, 5, 7, 11, 2, 5, 9, 4 |
| B. | 6, 5, 2, 11, 7, 4, 9, 5, 2 |
| C. | 2, 7, 2, 6, 5, 11, 5, 9, 4 |
| D. | none |
| Answer» A. 6, 2, 5, 7, 11, 2, 5, 9, 4 | |
| 97. |
For the tree below, write the level-order traversal. |
| A. | 2, 7, 2, 6, 5, 11, 5, 9, 4 |
| B. | 2, 7, 5, 2, 11, 9, 6, 5, 4 |
| C. | 2, 5, 11, 6, 7, 4, 9, 5, 2 |
| D. | none |
| Answer» B. 2, 7, 5, 2, 11, 9, 6, 5, 4 | |
| 98. |
What is the space complexity of the in-order traversal in the recursive fashion? (d is the tree depth and n is the number of nodes) |
| A. | O(1) |
| B. | O(nlogd) |
| C. | O(logd) |
| D. | O(d) |
| Answer» D. O(d) | |
| 99. |
What is the time complexity of level order traversal? |
| A. | O(1) |
| B. | O(n) |
| C. | O(logn) |
| D. | O(nlogn) |
| Answer» B. O(n) | |
| 100. |
Which of the following graph traversals closely imitates level order traversal of a binary tree? |
| A. | Depth First Search |
| B. | Breadth First Search |
| C. | Depth & Breadth First Search |
| D. | Binary Search |
| Answer» B. Breadth First Search | |
Done Studing? Take A Test.
Great job completing your study session! Now it's time to put your knowledge to the test. Challenge yourself, see how much you've learned, and identify areas for improvement. Don’t worry, this is all part of the journey to mastery. Ready for the next step? Take a quiz to solidify what you've just studied.