McqMate
210+ more mcqs Solved MCQs
in Problem Solving and Python ProgrammingThese multiple-choice questions (MCQs) are designed to enhance your knowledge and understanding in the following areas: Computer Science Engineering (CSE) , Information Technology Engineering (IT) , Electrical Engineering , Civil Engineering , Mechanical Engineering .
Chapters
| 151. |
What is the use of “a” in file handling? |
| A. | read |
| B. | write |
| C. | append |
| D. | none of the mentioned |
| Answer» C. append | |
| Explanation: this opens the fhe file in appending mode. that means, it will be open for writing and everything will be written to | |
| 152. |
Which function is used to read all the characters? |
| A. | read() |
| B. | readcharacters() |
| C. | readall() |
| D. | readchar() |
| Answer» A. read() | |
| Explanation: the read function reads all characters fh = open(“filename”, “r”) content = fh.read(). | |
| 153. |
Which function is used to read single line from file? |
| A. | readline() |
| B. | readlines() |
| C. | readstatement() |
| D. | readfullline() |
| Answer» B. readlines() | |
| Explanation: the readline function reads a single line from the file fh = open(“filename”, “r”) | |
| 154. |
Which function is used to write all the characters? |
| A. | write() |
| B. | writecharacters() |
| C. | writeall() |
| D. | writechar() |
| Answer» A. write() | |
| Explanation: to write a fixed sequence of characters to a file | |
| 155. |
Which function is used to write a list of string in a file? |
| A. | writeline() |
| B. | writelines() |
| C. | writestatement() |
| D. | writefullline() |
| Answer» A. writeline() | |
| Explanation: with the writeline function you can write a list of strings to a file | |
| 156. |
Which function is used to close a file in python? |
| A. | close() |
| B. | stop() |
| C. | end() |
| D. | closefile() |
| Answer» A. close() | |
| Explanation: f.close()to close it and free up any system resources taken up by the open file. | |
| 157. |
Is it possible to create a text file in python? |
| A. | yes |
| B. | no |
| C. | machine dependent |
| D. | all of the mentioned |
| Answer» A. yes | |
| Explanation: yes we can create a file in python. creation of file is as shown below. file = open(“newfile.txt”, “w”) file.write(“hello world in the new file\n”) file.write(“and another line\n”) file.close(). | |
| 158. |
Which of the following are the modes of both writing and reading in binary format in file? |
| A. | wb+ |
| B. | w |
| C. | wb |
| D. | w+ |
| Answer» A. wb+ | |
| Explanation: here is the description below “w” opens a file for writing only. overwrites the file if the file exists. if the file does not exist, creates a new file for writing. | |
| 159. |
Which of the following is not a valid mode to open a file? |
| A. | ab |
| B. | rw |
| C. | r+ |
| D. | w+ |
| Answer» B. rw | |
| Explanation: use r+, w+ or a+ to perform both read and write operations using a single file object. | |
| 160. |
Which of the following is not a valid attribute of a file object (fp)? |
| A. | fp.name |
| B. | fp.closed |
| C. | fp.mode |
| D. | fp.size |
| Answer» D. fp.size | |
| Explanation: fp.size has not been implemented. | |
| 161. |
How do you close a file object (fp)? |
| A. | close(fp) |
| B. | fclose(fp) |
| C. | fp.close() |
| D. | fp. close () |
| Answer» C. fp.close() | |
| Explanation: close() is a method of the file object. | |
| 162. |
How do you get the current position within the file? |
| A. | fp.seek() |
| B. | fp.tell() |
| C. | fp.loc |
| D. | fp.pos |
| Answer» B. fp.tell() | |
| Explanation: it gives the current position as an offset from the start of file. | |
| 163. |
How do you rename a file? |
| A. | fp.name = ‘new_name.txt’ |
| B. | os.rename(existing_name, new_name) |
| C. | os.rename(fp, new_name) |
| D. | os.set_name(existing_name, new_name) |
| Answer» B. os.rename(existing_name, new_name) | |
| Explanation: os.rename() is used to rename files. | |
| 164. |
How do you delete a file? |
| A. | del(fp) |
| B. | fp.delete() |
| C. | os.remove(‘file’) |
| D. | os.delete(‘file’) |
| Answer» C. os.remove(‘file’) | |
| Explanation: os.remove() is used to delete files. | |
| 165. |
How do you change the file position to an offset value from the start? |
| A. | fp.seek(offset, 0) |
| B. | fp.seek(offset, 1) |
| C. | fp.seek(offset, 2) |
| D. | none of the mentioned |
| Answer» A. fp.seek(offset, 0) | |
| Explanation: 0 indicates that the offset is with respect to the start. | |
| 166. |
What happens if no arguments are passed to the seek function? |
| A. | file position is set to the start of file |
| B. | file position is set to the end of file |
| C. | file position remains unchanged |
| D. | error |
| Answer» D. error | |
| Explanation: seek() takes at least one argument. | |
| 167. |
Which function overloads the == operator? |
| A. | eq () |
| B. | equ () |
| C. | isequal () |
| D. | none of the mentioned |
| Answer» A. eq () | |
| Explanation: the other two do not exist. | |
| 168. |
Which operator is overloaded by lg ()? |
| A. | < |
| B. | > |
| C. | != |
| D. | none of the mentioned |
| Answer» D. none of the mentioned | |
| Explanation: lg () is invalid. | |
| 169. |
Which function overloads the >> operator? |
| A. | more () |
| B. | gt () |
| C. | ge () |
| D. | none of the mentioned |
| Answer» D. none of the mentioned | |
| Explanation: rshift () overloads the >> operator. | |
| 170. |
Let A and B be objects of class Foo. Which functions are called when print(A + B) is executed? |
| A. | add (), str () |
| B. | str (), add () |
| C. | sum (), str () |
| D. | str (), sum () |
| Answer» A. add (), str () | |
| Explanation: the function add () is called first since it is within the bracket. the function str () is then called on the object that we received after adding a and b. | |
| 171. |
Which function overloads the // operator? |
| A. | div () |
| B. | ceildiv () |
| C. | floordiv () |
| D. | truediv () |
| Answer» C. floordiv () | |
| Explanation: floordiv () is for //. | |
| 172. |
How many except statements can a try- except block have? |
| A. | zero |
| B. | one |
| C. | more than one |
| D. | more than zero |
| Answer» D. more than zero | |
| Explanation: there has to be at least one except statement. | |
| 173. |
When is the finally block executed? |
| A. | when there is no exception |
| B. | when there is an exception |
| C. | only if some condition that has been specified is satisfied |
| D. | always |
| Answer» D. always | |
| Explanation: the finally block is always executed. | |
| 174. |
What happens when ‘1’ == 1 is executed? |
| A. | we get a true |
| B. | we get a false |
| C. | an typeerror occurs |
| D. | a valueerror occurs |
| Answer» B. we get a false | |
| Explanation: it simply evaluates to false and does not raise any exception. | |
| 175. |
Which of the following is not an exception handling keyword in Python? |
| A. | try |
| B. | except |
| C. | accept |
| D. | finally |
| Answer» C. accept | |
| Explanation: the keywords ‘try’, ‘except’ and ‘finally’ are exception handling keywords in python whereas the word ‘accept’ is not a keyword at all. | |
| 176. |
)) type(g) |
| A. | class <’loop’> |
| B. | class <‘iteration’> |
| C. | class <’range’> |
| D. | class <’generator’> |
| Answer» D. class <’generator’> | |
| Explanation: another way of creating a generator is to use parenthesis. hence the output of the code shown above is: class<’generator’>. | |
| 177. |
+ '3' |
| A. | nameerror |
| B. | indexerror |
| C. | valueerror |
| D. | typeerror |
| Answer» D. typeerror | |
| Explanation: the line of code shown above will result in a type error. this is because the operand ‘+’ is not supported when we combine the data types ‘int’ and ‘str’. sine this is exactly what we have done in the code shown above, a type error is thrown. | |
| 178. |
43') |
| A. | importerror |
| B. | valueerror |
| C. | typeerror |
| D. | nameerror |
| Answer» B. valueerror | |
| Explanation: the snippet of code shown above results in a value error. this is because there is an invalid literal for int() with base 10: ’65.43’. | |
| 179. |
Which of the following statements is true? |
| A. | the standard exceptions are automatically imported into python programs |
| B. | all raised standard exceptions must be handled in python |
| C. | when there is a deviation from the rules of a programming language, a semantic error is thrown |
| D. | if any exception is thrown in try block, else block is executed |
| Answer» A. the standard exceptions are automatically imported into python programs | |
| Explanation: when any exception is thrown in try block, except block is executed. if exception in not thrown in try block, else block is executed. when there is a deviation from the rules of a programming language, a | |
| 180. |
Which of the following is not a standard exception in Python? |
| A. | nameerror |
| B. | ioerror |
| C. | assignmenterror |
| D. | valueerror |
| Answer» C. assignmenterror | |
| Explanation: nameerror, ioerror and valueerror are standard exceptions in python whereas assignment error is not a standard exception in python. | |
| 181. |
Syntax errors are also known as parsing errors. |
| A. | true |
| B. | false |
| Answer» A. true | |
| Explanation: syntax errors are known as parsing errors. syntax errors are raised when there is a deviation from the rules of a language. hence the statement is true. | |
| 182. |
An exception is |
| A. | an object |
| B. | a special function |
| C. | a standard module |
| D. | a module |
| Answer» A. an object | |
| Explanation: an exception is an object that is raised by a function signaling that an unexpected situation has occurred, that the function itself cannot handle. | |
| 183. |
exceptions are raised as a result of an error in opening a particular file. |
| A. | valueerror |
| B. | typeerror |
| C. | importerror |
| D. | ioerror |
| Answer» D. ioerror | |
| Explanation: ioerror exceptions are raised as a result of an error in opening or closing a particular file. | |
| 184. |
Which of the following blocks will be executed whether an exception is thrown or not? |
| A. | except |
| B. | else |
| C. | finally |
| D. | assert |
| Answer» C. finally | |
| Explanation: the statements in the finally block will always be executed, whether an exception is thrown or not. this clause is used to close the resources used in a code. | |
| 185. |
Which of these definitions correctly describes a module? |
| A. | denoted by triple quotes for providing the specification of certain program elements |
| B. | design and implementation of specific functionality to be incorporated into a program |
| C. | defines the specification of how it is to be used |
| D. | any program that reuses code |
| Answer» B. design and implementation of specific functionality to be incorporated into a program | |
| Explanation: the term “module” refers to the implementation of specific functionality to be incorporated into a program. | |
| 186. |
Which of the following is not an advantage of using modules? |
| A. | provides a means of reuse of program code |
| B. | provides a means of dividing up tasks |
| C. | provides a means of reducing the size of the program |
| D. | provides a means of testing individual parts of the program |
| Answer» C. provides a means of reducing the size of the program | |
| Explanation: the total size of the program remains the same regardless of whether modules are used or not. modules simply divide the program. | |
| 187. |
Program code making use of a given module is called a of the module. |
| A. | client |
| B. | docstring |
| C. | interface |
| D. | modularity |
| Answer» A. client | |
| Explanation: program code making use of a given module is called the client of the module. there may be multiple clients for a module. | |
| 188. |
is a string literal denoted by triple quotes for providing the specifications of certain program elements. |
| A. | interface |
| B. | modularity |
| C. | client |
| D. | docstring |
| Answer» D. docstring | |
| Explanation: docstring used for providing the specifications of program elements. | |
| 189. |
Which of the following is true about top- down design process? |
| A. | the details of a program design are addressed before the overall design |
| B. | only the details of the program are addressed |
| C. | the overall design of the program is addressed before the details |
| D. | only the design of the program is addressed |
| Answer» C. the overall design of the program is addressed before the details | |
| Explanation: top-down design is an approach for deriving a modular design in which the overall design. | |
| 190. |
In top-down design every module is broken into same number of submodules. |
| A. | true |
| B. | false |
| Answer» B. false | |
| Explanation: in top-down design every module can even be broken down into different number of submodules. | |
| 191. |
All modular designs are because of a top- down design process. |
| A. | true |
| B. | false |
| Answer» B. false | |
| Explanation: the details of the program can be addressed before the overall design too. | |
| 192. |
Which of the following is not a valid namespace? |
| A. | global namespace |
| B. | public namespace |
| C. | built-in namespace |
| D. | local namespace |
| Answer» B. public namespace | |
| Explanation: during a python program execution, there are as many as three namespaces – built-in namespace, global namespace and local namespace. | |
| 193. |
Which of the following is false about “import modulename” form of import? |
| A. | the namespace of imported module becomes part of importing module |
| B. | this form of import prevents name clash |
| C. | the namespace of imported module becomes available to importing module |
| D. | the identifiers in module are accessed as: modulename.identifier |
| Answer» A. the namespace of imported module becomes part of importing module | |
| Explanation: in the “import modulename” form of import, the namespace of imported module becomes available to, but not part of, the importing module. | |
| 194. |
Which of the following is false about “from-import” form of import? |
| A. | the syntax is: from modulename import identifier |
| B. | this form of import prevents name clash |
| C. | the namespace of imported module becomes part of importing module |
| D. | the identifiers in module are accessed directly as: identifier |
| Answer» B. this form of import prevents name clash | |
| Explanation: in the “from-import” form of import, there may be name clashes because names of the imported identifiers aren’t specified along with the module name. | |
| 195. |
Which of the statements about modules is false? |
| A. | in the “from-import” form of import, identifiers beginning with two underscores are private and aren’t imported |
| B. | dir() built-in function monitors the items in the namespace of the main module |
| C. | in the “from-import” form of import, all identifiers regardless of whether they are private or public are imported |
| D. | when a module is loaded, a compiled version of the module with file extension .pyc is automatically produced |
| Answer» C. in the “from-import” form of import, all identifiers regardless of whether they are private or public are imported | |
| Explanation: in the “from-import” form of import, identifiers beginning with two underscores are private and aren’t imported. | |
| 196. |
What is the order of namespaces in which Python looks for an identifier? |
| A. | python first searches the global namespace, then the local namespace and finally the built- in namespace |
| B. | python first searches the local namespace, then the global namespace and finally the built-in namespace |
| C. | python first searches the built-in namespace, then the global namespace and finally the local namespace |
| D. | python first searches the built-in namespace, then the local namespace and finally the global namespace |
| Answer» B. python first searches the local namespace, then the global namespace and finally the built-in namespace | |
| Explanation: python first searches for the local, then the global and finally the built-in namespace. | |
| 197. |
What type of a structure is this?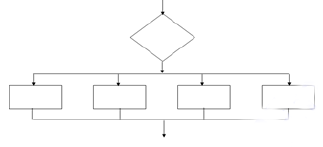
|
| A. | sequence |
| B. | case |
| C. | repetition |
| D. | process |
| Answer» B. case | |
| Explanation: This is a case structure. Certain cases are given along with a default case in the case structure | |
| 198. |
are identified by their addresses, we give them names (field names / variable names) using words. |
| A. | memory variables |
| B. | memory locations |
| C. | memory addresses |
| D. | data variables |
| Answer» B. memory locations | |
| 199. |
Operators with the same precedence are evaluated in which manner? |
| A. | left to right |
| B. | right to left |
| C. | can’t say |
| D. | none of the mentioned |
| Answer» A. left to right | |
| 200. |
The expression Int(x) implies that the variable x is converted to integer. |
| A. | true |
| B. | false |
| Answer» A. true | |
Done Studing? Take A Test.
Great job completing your study session! Now it's time to put your knowledge to the test. Challenge yourself, see how much you've learned, and identify areas for improvement. Don’t worry, this is all part of the journey to mastery. Ready for the next step? Take a quiz to solidify what you've just studied.