McqMate
177
101.8k
170+ Metrology and Measurements Solved MCQs
These multiple-choice questions (MCQs) are designed to enhance your knowledge and understanding in the following areas: Mechanical Engineering .
| 51. |
Which technique is not suitable to measure large diameter parts or large gaps? |
| A. | diffraction pattern technique |
| B. | scanning laser technique |
| C. | photodiode array imaging |
| D. | laser triangulation sensor |
| Answer» A. diffraction pattern technique | |
| Explanation: diffraction pattern technique is not suitable for diameters larger than few mm and is used to measure small gaps and small diameter parts. in this method, a parallel laser beam which is coherent is diffracted by a small part, and the resultant pattern is focussed on a linear diode array by a lens. | |
| 52. |
Which of the following is true about resolution in two frequency laser interferometer? |
| A. | straightness resolution – 90 nm |
| B. | angular resolution – 3 arc seconds |
| C. | flatness resolution – 2 nm |
| D. | linear resolution – 1 nm |
| Answer» D. linear resolution – 1 nm | |
| Explanation: the advantage of two frequency laser interferometer technique is that system does not depend upon the beam intensity and provides high sensitivity, it is also independent of noise due to air turbulence. the linear resolution by two frequency laser interferometer technique is 1 nm, angular resolution is 0.03 arc seconds and straightness resolution is 40 nm. | |
| 53. |
How much accuracy can be achieved by photodiode array imaging? |
| A. | ±0.05 μm |
| B. | ±0.15 μm |
| C. | ±0.5 μm |
| D. | ±0.25 μm |
| Answer» A. ±0.05 μm | |
| Explanation: in photodiode array imaging method which is a laser inspection technique in which the stationary part’s shadow is projected on a solid-state diode array image sensor. for large parts, 2 arrays are used i.e. one array for each edge. accuracies as high as ±0.05 μm can be achieved by this method. | |
| 54. |
Which application is ideally suited for two frequency laser interferometer? |
| A. | pitch and yaw measurement |
| B. | hole diameters |
| C. | thickness measurement |
| D. | measurement of edge locations |
| Answer» A. pitch and yaw measurement | |
| Explanation: 2 frequency laser interferometer techniques are ideally suitable for measuring linear positioning, pitch, yaw and straightness in two planes. the two- frequency laser head provides, one frequency with a p polarisation i.e. m (measuring) beam and another frequency with an s polarisation | |
| 55. |
The location of the image spot directly depends on which factor in laser triangulation sensor technique? |
| A. | wavelength of laser |
| B. | measuring range |
| C. | standoff distance |
| D. | focal length of lense |
| Answer» C. standoff distance | |
| Explanation: the location of the image spot in laser triangulation sensor technique depends directly upon the standoff distance between the sensor and the surface of object. if standoff distance changes, it will result in a lateral shift of the spot along the sensor array. | |
| 56. |
Which technique from given laser inspection techniques is useful for measuring the diameter of hot steel bars? |
| A. | laser scanning gauge |
| B. | frequency laser interferometer |
| C. | laser triangulation sensors |
| D. | photodiode array imaging |
| Answer» A. laser scanning gauge | |
| Explanation: the laser scanning gauge technique is very useful to measure the diameter and roundness of hot steel bars under the vibration conditions to an accuracy of 0.025 millimeter over diameters of 5 to 25 millimeter. | |
| 57. |
Where does wire is placed in a measurement of diameter using the technique of gauging wide diameter from the diffraction pattern formed in a laser beam? |
| A. | between collimator and lens |
| B. | between collimator and source |
| C. | between collimator and plane of measurement |
| D. | between collimator and detectors |
| Answer» C. between collimator and plane of measurement | |
| Explanation: gauging wide diameter is a method of the measurement of the thin wire diameter with the use of the interference fringes resulting from diffraction by the wire in the laser beam. output variation from the photodetector is caused by changes in fringes. | |
| 58. |
How many sensors are needed to measure part thickness by using laser triangulation sensors? |
| A. | 1 |
| B. | 2 |
| C. | 3 |
| D. | 4 |
| Answer» B. 2 | |
| Explanation: it is possible to measure part thickness or the inside bore diameter with the help of 2 sensors in laser triangulation sensor technique. the measurement accuracy and measurement range are directly related. | |
| 59. |
What precise movement does CMM have? |
| A. | precise movement in x coordinate |
| B. | precise movement in x and y coordinates |
| C. | precise movement in y and z coordinates |
| D. | precise movement in x, y and z coordinates |
| Answer» D. precise movement in x, y and z coordinates | |
| Explanation: co-ordinate measuring machines are useful for three dimensional measurements. these machines have precise movements in x,y and z coordinates which can be easily measured and controlled. | |
| 60. |
Which type of CMM is most suited for large heavy workpieces? |
| A. | cantilever type |
| B. | bridge type |
| C. | horizontal boring mill type |
| D. | floating bridge type |
| Answer» C. horizontal boring mill type | |
| Explanation: bridge type cmm is more difficult to load. it less sensitive to mechanical errors. horizontal boring mill type is best suited for heavy and large workpieces. highly accurate type is vertical bore mill type but is usually slower to operate. | |
| 61. |
Which direction is sensed by a linear measurement transducer used in CMM? |
| A. | positive direction only |
| B. | negative direction only |
| C. | both positive and negative direction |
| D. | not used to sense directions |
| Answer» C. both positive and negative direction | |
| Explanation: each slide in cmm is equipped with the help of a precision linear measurement transducer in 3 directions. it | |
| 62. |
What is the accuracy of present day co- ordinate measuring machine? |
| A. | 10 microns |
| B. | 5 microns |
| C. | 2 microns |
| D. | 1 micron |
| Answer» A. 10 microns | |
| Explanation: co-ordinate measuring machines of present day are three-axis digital read-out type and these machines work up with an accuracy of 10 microns. resolution of present day co-ordinate machine is 5 microns. | |
| 63. |
What is the name of an element which uses inductive coupling? |
| A. | inducto conduct |
| B. | inductosyn |
| C. | conductosyn |
| D. | conducto induct |
| Answer» B. inductosyn | |
| Explanation: cmm utilize a measuring element known as inductosyn data element. it uses inductive coupling between conductors and the conductors are separated by a small air gap. as inductosyn is not subjected to wear, it does not develop inaccuracy. | |
| 64. |
Which principle is used in the three master guideways and probe location? |
| A. | principle of dynamic design |
| B. | principle of static design |
| C. | principle of kinematic design |
| D. | principle of effective design |
| Answer» C. principle of kinematic design | |
| Explanation: in the probe location and three master guideways, the principles of kinematic design are used. whole machine is supported on a 3-point suspension with its massive granite work table. | |
| 65. |
What is the cause of translational errors in CMM? |
| A. | error in scale division |
| B. | error in straightness |
| C. | twisting error |
| D. | roll error |
| Answer» B. error in straightness | |
| Explanation: translational errors result from errors in the division of scale and straightness error perpendicular to the corresponding axis direction. errors in scale division are known as positional errors. error in straightness is the cause of translational errors. | |
| 66. |
Which of the following is not related to the geometrical accuracy of CMM? |
| A. | straightness of axes |
| B. | squareness of axes |
| C. | position accuracy |
| D. | axial length measuring accuracy |
| Answer» D. axial length measuring accuracy | |
| Explanation: geometrical accuracy concerned with the straightness of axes, position accuracy and squareness of axes while total measuring accuracy concerns volumetric length measuring accuracy and axial length measuring accuracy. | |
| 67. |
How many measurement parameters are considered in checking axes accuracy of straightness in CMM? |
| A. | 2 |
| B. | 4 |
| C. | 6 |
| D. | 8 |
| Answer» C. 6 | |
| Explanation: six measurement parameters need to be considered in the straightness of axes. straightness of x-axis measured in y and z directions. straightness of z-axis in x and y directions and of y-axis in x and z directions. | |
| 68. |
How many reference gauges are measured for volumetric length measuring accuracy in CMM? |
| A. | 2 |
| B. | 3 |
| C. | 4 |
| D. | 5 |
| Answer» B. 3 | |
| Explanation: it is defined as the difference between the reference length of gauges, oriented freely and the corresponding results from the machine. 3 reference gauges are measured. their lengths corresponding to approx. 1/3, 1/2 and 3/4 of the full travel of the longest axes. | |
| 69. |
Which of the following is true for trigger type probe system used in computer controlled CMM? |
| A. | bucking mechanism is a 2 point bearing |
| B. | current coordinate position stored when circuit is close |
| C. | contacts of point bearing arranged at 90 degree |
| D. | contacts of point bearing act as electrical micro switches |
| Answer» D. contacts of point bearing act as electrical micro switches | |
| Explanation: the “buckling mechanism” in trigger type probe system is a 3 point bearing, the contacts of which are arranged around the circumference at 120 degrees. these contacts act as micro switches. | |
| 70. |
What does the total number of pixels in the region defines? |
| A. | perimeter |
| B. | area |
| C. | intensity |
| D. | brightness |
| Answer» B. area | |
| Explanation: the area of a region is defined by the total number of pixels in the region. the perimeter is given the number of pixels | |
| 71. |
What is the unit of compactness of a region? |
| A. | meter |
| B. | meter2 |
| C. | no units |
| D. | meter-1 |
| Answer» C. no units | |
| Explanation: the compactness of a region is defined as (perimeter)2/area. thus, the compactness of a region is a dimensionless quantity. | |
| 72. |
For which of the following regions, compactness is minimal? |
| A. | rectangle |
| B. | square |
| C. | irregular |
| D. | disk |
| Answer» D. disk | |
| Explanation: we know that, compactness of a region is defined as (perimeter)2/area. thus, disk shaped region has a minimal value of this ratio and hence the minimal compactness. | |
| 73. |
Compactness is insensitive to orientation. |
| A. | true |
| B. | false |
| Answer» A. true | |
| Explanation: with the exception of errors introduced by the rotation of the digital image, we can state that compactness of a region is insensitive to the orientation of the image. | |
| 74. |
Which of the following measures are not used to describe a region? |
| A. | mean and median of grey values |
| B. | minimum and maximum of grey values |
| C. | number of pixels alone |
| D. | number of pixels above and below mean |
| Answer» C. number of pixels alone | |
| Explanation: some of the measures which are used to describe a region are mean and median of grey values, minimum and maximum of grey values and number of pixels above and below mean. the area of the region, i.e., the total number of pixels in the region cannot alone describe the region. | |
| 75. |
We cannot use normalized area as one of the region descriptor. |
| A. | true |
| B. | false |
| Answer» B. false | |
| Explanation: one of the regional descriptor is normalized area. it can be quite useful to extract information from the image. in satellite images of earth, the data can be refined by normalized it with respect to land mass per region. | |
| 76. |
What is the study of properties of a figure that are unaffected by any deformation? |
| A. | topology |
| B. | geography |
| C. | statistics |
| D. | deformation |
| Answer» A. topology | |
| Explanation: we can define topology as the study of properties of a figure that are unaffected by any deformation, as long as there is no joining or tearing of the figure. we use topological properties in the region description. | |
| 77. |
On which of the following operation of an image, the topology of the region changes? |
| A. | stretching |
| B. | rotation |
| C. | folding |
| D. | change in distance measure |
| Answer» C. folding | |
| Explanation: if a topological descriptor is defined by the number of holes in an image, then the number of holes will not vary if the | |
| 78. |
Topological properties don’t depend on the distance measures. |
| A. | true |
| B. | false |
| Answer» A. true | |
| Explanation: we know that, as stretching affects distance, topological properties do not depend on the notion of distance or any properties implicitly based on the concept of distance measures. | |
| 79. |
What is the Euler number of the image shown below?
|
| A. | 0 |
| B. | 1 |
| C. | 2 |
| D. | -1 |
| Answer» D. -1 | |
| Explanation: the image shown in the question has two holes and one connected components. so, the euler number e is given as 1-2=-1. | |
| 80. |
What is the Euler number of a region with polygonal network containing V,Q and F as the number of vertices, edges and faces respectively? |
| A. | v+q+f |
| B. | v-q+f |
| C. | v+q-f |
| D. | v-q-f |
| Answer» B. v-q+f | |
| Explanation: it is very important to classify the polygonal network. let v,q and f denote | |
| 81. |
What is the Euler number of the region shown in the figure below?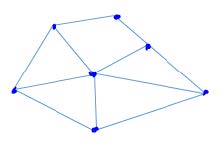
|
| A. | 1 |
| B. | -2 |
| C. | -1 |
| D. | 2 |
| Answer» B. -2 | |
| Explanation: the polygonal network given in the figure has 7 vertices, 11 edges and 2 faces. thus the euler number is given by the formula, | |
| 82. |
The texture of the region provides measure of which of the following properties? |
| A. | smoothness alone |
| B. | coarseness alone |
| C. | regularity alone |
| D. | smoothness, coarseness and regularity |
| Answer» D. smoothness, coarseness and regularity | |
| Explanation: one of the important approach to region description is texture content. this helps to provide the measure of some of the important properties of an image like smoothness, coarseness and regularity of the region. | |
| 83. |
Structural techniques deal with the arrangement of image primitives. |
| A. | true |
| B. | false |
| Answer» A. true | |
| Explanation: structural techniques deal with the arrangement of image primitives, such as the description of the texture based on the regularly spaced parallel lines. | |
| 84. |
Which of the following techniques is based on the Fourier transform? |
| A. | structural |
| B. | spectral |
| C. | statistical |
| D. | topological |
| Answer» B. spectral | |
| Explanation: spectral techniques are based on properties of the fourier spectrum and are used primarily to detect global periodicity in an image by identifying high energy, narrow peaks in the image. | |
| 85. |
Who gave the fundamental principle of straightness measurement? |
| A. | bryan |
| B. | moire |
| C. | euler |
| D. | amedeo |
| Answer» A. bryan | |
| Explanation: fundamental principle of measurement of straightness is given by bryan. according to this principle, “a straightness measurement system should be in | |
| 86. |
Which of the following represents the quality of straightness in precision engineering? |
| A. | spirit level |
| B. | straight edge |
| C. | autocollimator |
| D. | dial indicator |
| Answer» B. straight edge | |
| Explanation: at many places, it is necessary that the surface must be straight e.g. in lathe machine it is required that the tool must move in straight path. straight line is the basis of most methods of measurements. | |
| 87. |
What is the tolerance of the straightness of a line? |
| A. | maximum deviation from the straight line joining two extremities |
| B. | maximum deviation from the middle point of straight line joining two extremities |
| C. | minimum deviation from the straight line joining two extremities |
| D. | minimum deviation from the middle point of straight line joining two extremities |
| Answer» A. maximum deviation from the straight line joining two extremities | |
| Explanation: the tolerance on the straightness of a line can be defined as the maximum deviation in | |
| 88. |
What is the name of a pair of straight edges? |
| A. | drum sticks |
| B. | lower pair |
| C. | winding sticks |
| D. | self closed pair |
| Answer» C. winding sticks | |
| Explanation: straight edge is a measuring tool consist of a steel and is used to check the straightness. straight edges are used in machining industry and automotive service. winding stick is a pair of straight edges which are used in woodwork. | |
| 89. |
What is the position of straightness interferometer in straightness measurement optics? |
| A. | before laser head |
| B. | after straightness reflector |
| C. | between laser head and straightness reflector |
| D. | no need of interferometer |
| Answer» C. between laser head and straightness reflector | |
| Explanation: straightness interferometer is placed between laser head and reflector. | |
| 90. |
What is the range of straightness measurement in straightness measurement optics? |
| A. | ±2.5 mm |
| B. | ±5 mm |
| C. | ±10 mm |
| D. | ±20 mm |
| Answer» A. ±2.5 mm | |
| Explanation: to measure straightness errors in a linear axis, straightness measurement optics are used. for both short range and long range measurement, length of straightness measurement is ±2.5 mm. | |
| 91. |
Which of the following is not the factor affecting the accuracy of straightness measurement by optics? |
| A. | air turbulence |
| B. | optics fixed rigidly |
| C. | slope error |
| D. | localised heat sources |
| Answer» B. optics fixed rigidly | |
| Explanation: factors affecting the accuracy of straightness measurement by optics are air turbulence, mechanical vibrations, optic errors, slope errors, optics not fixed in the correct position, optics not fixed rigidly, localised heat sources etc. | |
| 92. |
At which part of the precision straight edge is generally lapped? |
| A. | edges only |
| B. | base only |
| C. | base and edges both |
| D. | all over the surface |
| Answer» A. edges only | |
| Explanation: straight edges are extremely useful for setting up machines such as planers. precision straight edges are hardened and lapped on the edges by a small radius, which makes a blunt knife edge straight to a few thousands of an mm. | |
| 93. |
What type of thread is formed on female screw gauge? |
| A. | external thread |
| B. | internal thread |
| C. | both internal and external |
| D. | major screw thread |
| Answer» B. internal thread | |
| Explanation: an internal thread is that which formed on the inside of a workpiece e.g. on female screw gauge or a nut. an external thread is that which formed on the outside of a workpiece e.g on bolts or studs. | |
| 94. |
Which of the following option is true for truncation? |
| A. | thread can be tranculated at crest only |
| B. | thread can be tranculatd at root only |
| C. | thread can be tranculated at crest and root both |
| D. | thread can’t be tranculated at crest and root both |
| Answer» C. thread can be tranculated at crest and root both | |
| Explanation: a thread is truncated sometimes at the crest or at the root or at both root and crest and root. the radial distance from the crest to the nearest apex of the fundamental triangle is truncation at the crest is and at the root it is the radial distance from the root to the nearest apex. | |
| 95. |
What is dedendum for external threads? |
| A. | radial distance between pitch and minor cylinder |
| B. | radial distance between major and pitch cylinder |
| C. | radial distance between major and minor cylinder |
| D. | axial distance between major and pitch cylinder |
| Answer» A. radial distance between pitch and minor cylinder | |
| Explanation: addendum for an external thread is defined as the radial distance between the major cylinder and pitch cylinder and for internal addendum is the radial distance between the minor cylinder and pitch cylinder. dedendum for external thread is the radial distance between the pitch cylinder and minor cylinder and this is the radial distance between the major and pitch cylinders for internal thread. | |
| 96. |
Which of the following is not a name of the major diameter of an external thread? |
| A. | outside diameter |
| B. | crest diameter |
| C. | full diameter |
| D. | cone diameter |
| Answer» D. cone diameter | |
| Explanation: for a straight thread, major diameter is the diameter of the major cylinder. it is also known to as the outside diameter or full diameter for external threads. sometimes it is also called crest diameter. | |
| 97. |
Which of the following is not true about the axial thickness of screw thread? |
| A. | measured in direction perpendicular to the axis of thread |
| B. | measured on pitch cylinder |
| C. | distance between opposite faces of same thread |
| D. | measured at the same thread |
| Answer» A. measured in direction perpendicular to the axis of thread | |
| Explanation: in a screw thread axial thickness is the distance between the opposite faces of the same thread. it is measured on the pitch cylinder and in a direction parallel to the thread axis. | |
| 98. |
What is the alternative name of functional diameter? |
| A. | cone diameter |
| B. | virtual diameter |
| C. | root diameter |
| D. | inside diameter |
| Answer» B. virtual diameter | |
| Explanation: functional diameter is also known as virtual diameter. for an internal or external thread, this is the pitch diameter of the enveloping thread, lead and flank angles having the full depth of engagement but not at roots and crests. | |
| 99. |
What is a thread per inch in screw thread? |
| A. | pitch in inches |
| B. | axial distance moved by threaded part |
| C. | reciprocal of pitch in inches |
| D. | radial distance moved by threaded part |
| Answer» C. reciprocal of pitch in inches | |
| Explanation: thread per inch is the reciprocal of the pitch(inches). the angle made by the thread helix at the pitch line with plane perpendicular to the axis is known as lead angle. lead angle is measured in an axial plane. | |
| 100. |
Which of the following is not true about effective diameter? |
| A. | also known as pitch diameter |
| B. | it decides quality of fit between nut and screw |
| C. | this is the diameter of minor cylinder |
| D. | it is a very important dimension for screw threads |
| Answer» C. this is the diameter of minor cylinder | |
| Explanation: in case of straight thread, effective diameter is the diameter of the pitch cylinder and is also called as pitch diameter. effective diameter is the most important dimension at it decides the quality of the fit between the nut and the screw. | |
Done Studing? Take A Test.
Great job completing your study session! Now it's time to put your knowledge to the test. Challenge yourself, see how much you've learned, and identify areas for improvement. Don’t worry, this is all part of the journey to mastery. Ready for the next step? Take a quiz to solidify what you've just studied.