McqMate
190
91.4k
180+ Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry 3 Solved MCQs
These multiple-choice questions (MCQs) are designed to enhance your knowledge and understanding in the following areas: Bachelor of Pharmacy (B. Pharma) , Pharmacy .
| 51. |
If a solution of a compound (30.0 g/100 mL of solution) has a measured rotation of +15º in a 2 dm tube, the specific rotation is: |
| A. | +50º |
| B. | +25º |
| C. | +15º |
| D. | +7.5º |
| Answer» B. +25º | |
| 52. |
In the absence of specific data, it can only be said that (R)–2–bromopentane is: |
| A. | dextrorotatory (+). |
| B. | levorotatory (–). |
| C. | analogous in absolute configuration to (R)–2–bromopentane. |
| D. | optically inactive. |
| Answer» C. analogous in absolute configuration to (R)–2–bromopentane. | |
| 53. |
Those stereoisomers which can be interconverted only by breaking and remaking of covalent bonds are called as____ |
| A. | Chain isomers |
| B. | Positional isomers |
| C. | Configurational isomers |
| D. | Conformational isomers |
| Answer» C. Configurational isomers | |
| 54. |
Those stereoisomers which can be interconverted by simple rotation about sigma bonds are called as____ |
| A. | Conformational isomers |
| B. | Functional isomers |
| C. | Geometric isomers |
| D. | Tautomers |
| Answer» A. Conformational isomers | |
| 55. |
A beam of light having a particular wavelength and having vibrations only in one plane is____ |
| A. | Ordinary light |
| B. | Plane polarized light |
| C. | Monochromatic light |
| D. | None of above |
| Answer» B. Plane polarized light | |
| 56. |
Optically active compound can rotate_____ |
| A. | Ordinary light |
| B. | Plane polarized light |
| C. | Monochromatic light |
| D. | None of above |
| Answer» B. Plane polarized light | |
| 57. |
Which instrument is used to measure angle of rotation? |
| A. | Polarimeter |
| B. | UV spectrometer |
| C. | pH meter |
| D. | Conductometer |
| Answer» A. Polarimeter | |
| 58. |
For being chiral compound, chemical compound should not possess following characteristic |
| A. | Plane of symmetry |
| B. | Centre of symmetry |
| C. | Axis of symmetry |
| D. | All of the above |
| Answer» D. All of the above | |
| 59. |
Followings are types of optical isomers except__ |
| A. | Enantiomers |
| B. | Diasteromers |
| C. | Conformers |
| D. | Meso compounds |
| Answer» C. Conformers | |
| 60. |
How many possible stereoisomers for the compound CH3CH(OH)COOH. |
| A. | 1 |
| B. | 2 |
| C. | 3 |
| D. | 4 |
| Answer» B. 2 | |
| 61. |
Which is the true option for Diastereomers? |
| A. | They have only one chiral centre. |
| B. | They have identical physical properties |
| C. | They have two or more chiral centre. |
| D. | All of the above. |
| Answer» C. They have two or more chiral centre. | |
| 62. |
Ratio of dextro and levo isomers (d:l) of compound present in raceme mixture is__ |
| A. | 50:50 |
| B. | 40:60 |
| C. | 30:70 |
| D. | 20:80 |
| Answer» A. 50:50 | |
| 63. |
The process of separation of a racemic mixture into optically active d and l isomers is___ |
| A. | Racemization |
| B. | Resolution |
| C. | Both (a) and (b) |
| D. | None of the above |
| Answer» B. Resolution | |
| 64. |
Absolute configuration of stereoisomer is denoted by__ |
| A. | R and S isomers |
| B. | D and L isomers |
| C. | d and l isomers |
| D. | cis and tr |
| Answer» A. R and S isomers | |
| 65. |
Relative configuration of stereoisomer is denoted by__ |
| A. | R and S isomers |
| B. | D and L isomers |
| C. | d and l isomers |
| D. | cis and tr |
| Answer» A. R and S isomers | |
| 66. |
The necessary conditions for geometric isomers are__ |
| A. | Presence of at least one double bond. |
| B. | Each carbon atom of the double bond should be linked to two different atoms or groups. |
| C. | Both (a) and (b) |
| D. | None of the above. |
| Answer» C. Both (a) and (b) | |
| 67. |
By studying which physical property, configuration of geometric isomers can be determined |
| A. | Melting point |
| B. | Solubility |
| C. | Dipole moment |
| D. | All of the above |
| Answer» D. All of the above | |
| 68. |
From the followings, which is true about conformational isomers? |
| A. | Eclipsed conformation is more stable than staggered conformation. |
| B. | Eclipsed conformation is less stable than staggered conformation. |
| C. | Eclipsed conformation has low energy than staggered conformation. |
| D. | None of the above |
| Answer» B. Eclipsed conformation is less stable than staggered conformation. | |
| 69. |
Most stable conformation of cyclohexane is___ |
| A. | Chair conformation |
| B. | Boat conformation |
| C. | Twist boat conformation |
| D. | Half chair conformation |
| Answer» A. Chair conformation | |
| 70. |
The hydrogens lying in the plane of the cyclohexane ring are called____ |
| A. | Axial hydrogens |
| B. | Chiral hydrogens |
| C. | Equatorial hydrogens |
| D. | None of the above |
| Answer» C. Equatorial hydrogens | |
| 71. |
The hydrogens lying above or below the plane of the cyclohexane ring are called____ |
| A. | Axial hydrogens |
| B. | Chiral hydrogens |
| C. | Equatorial hydrogens |
| D. | None of the above |
| Answer» A. Axial hydrogens | |
| 72. |
Which is the true sentence for stereospecific reactions from the followings, |
| A. | Reactants react at different rate i.e. they have different rate of reaction. |
| B. | They give different stereoisomers as products. |
| C. | They have different paths to give different types of compounds as products. |
| D. | All of the above |
| Answer» D. All of the above | |
| 73. |
Which of the following statements most accurately describes the stereochemistry between the various cyclohexanes? |
| A. | Cis-1,2-dichlorocyclohexane and trans-1,2-dichlorocyclohexane rotate plane-polarized light in opposite directions, and together in equal proportions form a racemic mixture. |
| B. | The diaxial and diequatorial forms of trans-1,3-dichlorohexane can be separated by their differing physical properties. |
| C. | Only cis-1,4-dichlorocyclohexane is achiral due to a plane of symmetry, and cis-1,4- dichlorocyclohexane is diastereomeric to trans-1,4-dichlorocyclohexane. |
| D. | The conformational isomers of tr |
| Answer» D. The conformational isomers of tr | |
| 74. |
Which of the following is the definition of a pair of diastereomers? |
| A. | A pair of stereoisomers each of which has two chirality centers |
| B. | Any pair of stereoisomers |
| C. | A pair of stereoisomers that are not mirror images of one another |
| D. | A pair of stereoisomers that are non-superimposable mirror images of one another |
| Answer» C. A pair of stereoisomers that are not mirror images of one another | |
| 75. |
What is the relation between the given compound?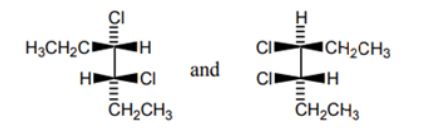
|
| A. | constitutional isomers |
| B. | enantiomers |
| C. | Diastereomers |
| D. | Identical |
| Answer» C. Diastereomers | |
| 76. |
What is the relation between the given compounds?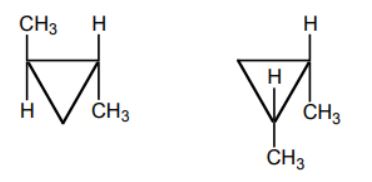
|
| A. | Diastereomers |
| B. | constitutional isomers |
| C. | enantiomers |
| D. | identical |
| Answer» A. Diastereomers | |
| 77. |
Which of the following statements regarding enantiomers not true? |
| A. | All (+) enantiomers are levorotatory |
| B. | All (-) enantiomers rotate plane polarized light in a clockwise direction |
| C. | (+) and (-) enantiomers rotate plane polarized light in opposite directions |
| D. | All R enantiomers are dextrorotatory |
| Answer» C. (+) and (-) enantiomers rotate plane polarized light in opposite directions | |
| 78. |
Which of the following is/are the S-enantiomer of alanine?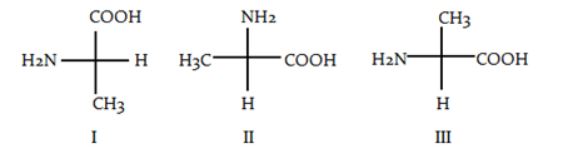
|
| A. | Only 1 |
| B. | Only 2 |
| C. | 1 and 3 |
| D. | 2 and 3 |
| Answer» C. 1 and 3 | |
| 79. |
Which of the following is capable of existing as a pair of enantiomers? |
| A. | 2-methylpropane |
| B. | 2-methylpentane |
| C. | 3-methylpentane |
| D. | 3-methylhexane |
| Answer» D. 3-methylhexane | |
| 80. |
Which statement about a chiral compound A is incorrect? |
| A. | A racemate contains equal amounts of (+)-A and (–)-A |
| B. | If A is resolved, it is separated into its enantiomers |
| C. | (+)-A can also be labelled R-A, because (+) means the same as R |
| D. | (+)-A and (–)-A will rotate polarized light equally but in opposite directions |
| Answer» D. (+)-A and (–)-A will rotate polarized light equally but in opposite directions | |
| 81. |
Which of the following is the definition of chirality? |
| A. | The superimposability of an object on its mirror image |
| B. | A molecule with a mirror image |
| C. | The non-superimposability an object on its mirror image |
| D. | A molecule that has a carbon atom with four different substituents |
| Answer» D. A molecule that has a carbon atom with four different substituents | |
| 82. |
Which symmetry element makes the given compound achiral?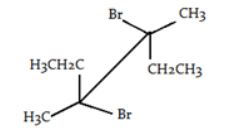
|
| A. | Plane of symmetry (POS) |
| B. | Center of symmetry (COS) |
| C. | Axis of symmetry (AOS) |
| D. | Alternating axis of symmetry (AAOS) |
| Answer» A. Plane of symmetry (POS) | |
| 83. |
Which of the following is the definition for enatiomerism? |
| A. | A pair of stereoisomers each of which has two chirality centres |
| B. | A pair of stereoisomers that are not mirror images of one another |
| C. | A pair of stereoisomers that are non-superimposable mirror images of one another |
| D. | Any pair of stereoisomers |
| Answer» C. A pair of stereoisomers that are non-superimposable mirror images of one another | |
| 84. |
Which of the following notations is not used to distinguish between pairs of enantiomers? |
| A. | R and S |
| B. | E and Z |
| C. | + and – |
| D. | D and L |
| Answer» B. E and Z | |
| 85. |
Which among the following is not true about enantiomerism? |
| A. | Assignments of R and S labels and (+) and (–) labels are not connected |
| B. | The labels R and S refer to different conformers |
| C. | The labels (+) and (–) are used to distinguish enantiomers |
| D. | The specific rotation of enantiomers is equal and opposite |
| Answer» B. The labels R and S refer to different conformers | |
| 86. |
Which of the following molecules does not possess enantiomers? |
| A. | CH3CH2CH2CHBrCH3 |
| B. | CH3CH2CBr2CH3 |
| C. | CH3CHBrCH2CH3 |
| D. | CHBr2CH2CHBrCH3 |
| Answer» B. CH3CH2CBr2CH3 | |
| 87. |
What does a polarimeter measure? |
| A. | Polarity of the substance |
| B. | Angle of rotation of an optical active compound |
| C. | Concentration of the substance |
| D. | pH of the substance |
| Answer» B. Angle of rotation of an optical active compound | |
| 88. |
A solution of 0.1 g/mL of a pure R enantiomer in a 1.0 dm (i.e., 10 cm) polarimeter rotates plane polarized light by +4.8°. What is the rotation observed on this solution in a 2 dm polarimeter? |
| A. | +2.4° |
| B. | +4.8° |
| C. | +19° |
| D. | +9.6° |
| Answer» D. +9.6° | |
| 89. |
. Polarimeter works on the principle of which of the following? |
| A. | polarization of light |
| B. | change of the electrical conductivity of solution with composition |
| C. | change of angle of refraction with composition |
| D. | change of electrical conductivity of solution with temperature |
| Answer» A. polarization of light | |
| 90. |
Which of the following groups has the highest priority according to the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog sequence rules? |
| A. | CH3 |
| B. | CH2Cl |
| C. | CH2OH |
| D. | CHO |
| Answer» D. CHO | |
| 91. |
What is the percent composition of a mixture of (S)-(+)-2-butanol, α= +13.52°, and (R)-(-)-2-butanol, α = -13.52°, with a specific rotation α = +6.76°? |
| A. | 75%(R) 25%(S) |
| B. | 25%(R) 75%(S) |
| C. | 50%(R) 50%(S) |
| D. | 67%(R) 33%(S) |
| Answer» A. 75%(R) 25%(S) | |
| 92. |
What can be said with certainty if a compound has α= -9.25°? |
| A. | The compound has the (S) configuration |
| B. | The compound has the (R) configuration |
| C. | The compound is not a meso form |
| D. | The compound possesses only one stereogenic center |
| Answer» C. The compound is not a meso form | |
| 93. |
Which of the following compounds can exhibit geometrical isomerism? |
| A. | 1-Hexene |
| B. | 2-Methyl-2-Pentene |
| C. | 3-methyl-1-pentene |
| D. | 2-Hexene |
| Answer» D. 2-Hexene | |
| 94. |
How many stereoisomers are there for the following structure?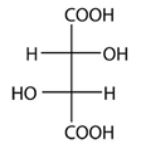
|
| A. | 1 |
| B. | 2 |
| C. | 3 |
| D. | 4 |
| Answer» C. 3 | |
| 95. |
How many stereoisomers of 3-bromo-2-butanol, CH3CH(OH)CHBrCH3, exist? |
| A. | 3 |
| B. | 1 |
| C. | 2 |
| D. | 4 |
| Answer» D. 4 | |
| 96. |
How many stereoisomers of 2,3-butanediol, CH3CH(OH)CH(OH)CH3, exist? |
| A. | 3 |
| B. | 4 |
| C. | 1 |
| D. | 2 |
| Answer» A. 3 | |
| 97. |
How many number of stereoisomers possible for 2, 3-pentanediol? |
| A. | 3 |
| B. | 4 |
| C. | 5 |
| D. | 6 |
| Answer» B. 4 | |
| 98. |
Which of the following is a not a five membered ring? |
| A. | Pyridine |
| B. | Pyrrole |
| C. | Furan |
| D. | Thiophene |
| Answer» A. Pyridine | |
| 99. |
Which of the following five membered a ring is most resonance stabilized? |
| A. | Furan |
| B. | Thiophene |
| C. | Pyrrole |
| D. | Pyridine |
| Answer» B. Thiophene | |
| 100. |
Five membered rings come under which category of heterocycle classification on the basis of chemical behavior? |
| A. | -excessive heterocycle |
| B. | -deficient heterocycle |
| C. | -equivalent heterocycle |
| D. | Can’t say about the five membered rings |
| Answer» A. -excessive heterocycle | |
Done Studing? Take A Test.
Great job completing your study session! Now it's time to put your knowledge to the test. Challenge yourself, see how much you've learned, and identify areas for improvement. Don’t worry, this is all part of the journey to mastery. Ready for the next step? Take a quiz to solidify what you've just studied.